Endless halfbetting#
from roulette import Roulette
from core import *
from simulations_core import get_mean_and_std_of_histories
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
roulette = Roulette()
def endless_half_betting(starting_money, bet_amount):
money = starting_money
money_points = [money]
while money != 0:
if money - bet_amount >= 0:
money += roulette.make_even_bet(bet_amount)
else:
money += roulette.make_even_bet(money)
money_points.append(money)
return money_points
money_histories = dict()
for i in range(10, 110, 10):
money_histories[i] = []
for bet_percentage in range(10, 110, 10):
for _ in range (1000):
money_histories[bet_percentage].append(endless_half_betting(100, bet_percentage))
for i in range(10, 110, 10):
mean_money_list, std_money_list = get_mean_and_std_of_histories(money_histories, i)
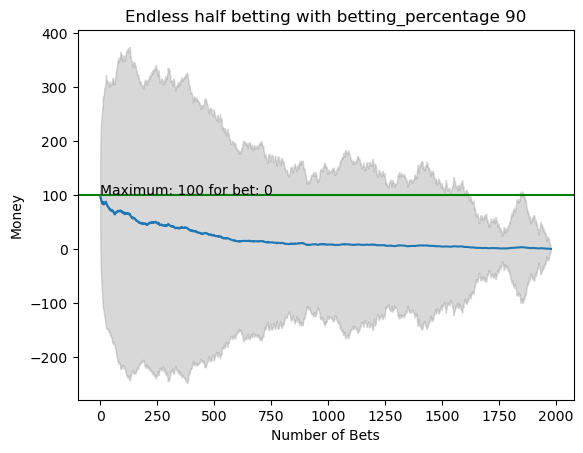
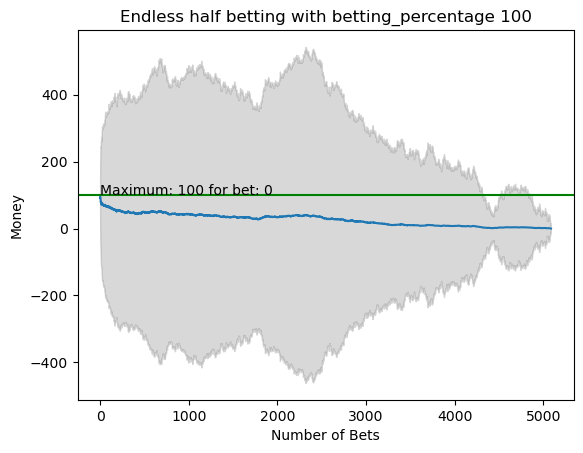
plot_money_history(mean_money_list, std_dev=std_money_list, title=f'Endless half betting with betting_percentage {i}', maximum_line=True)
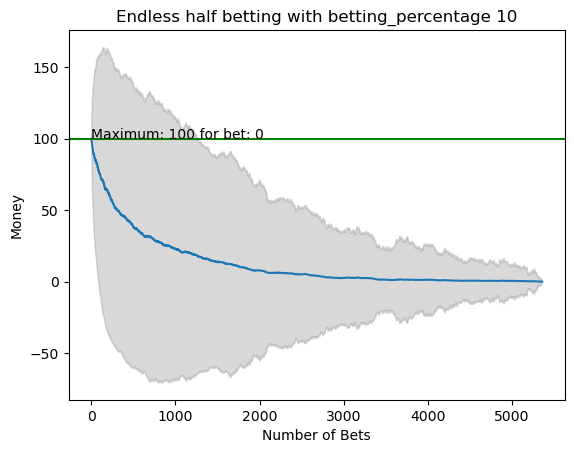
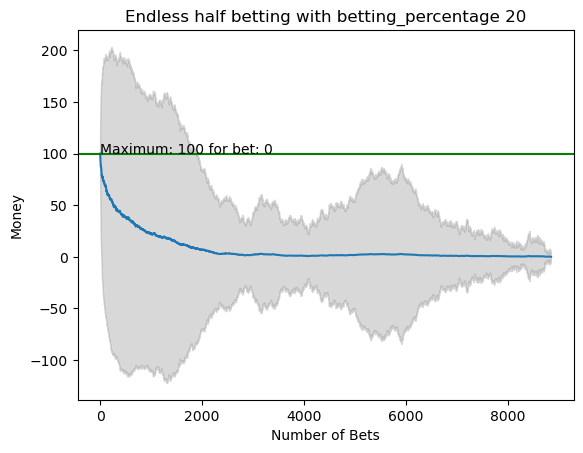
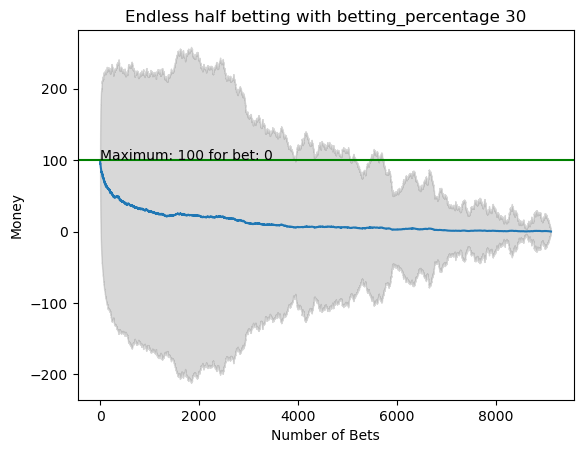
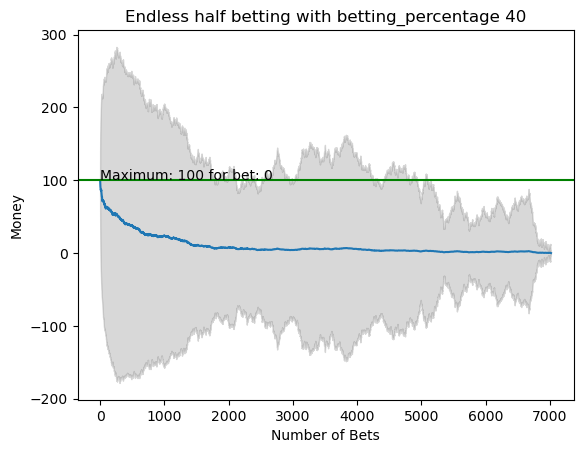
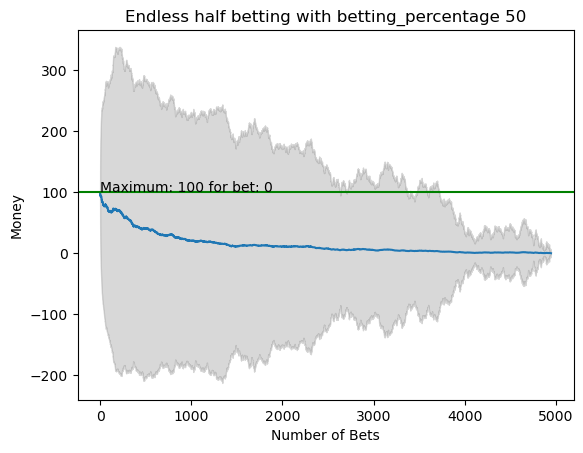
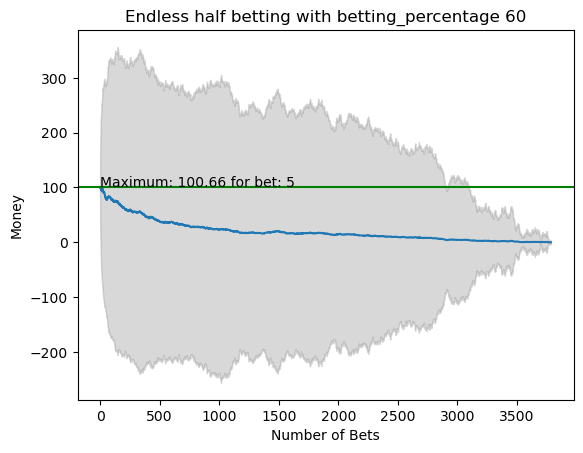
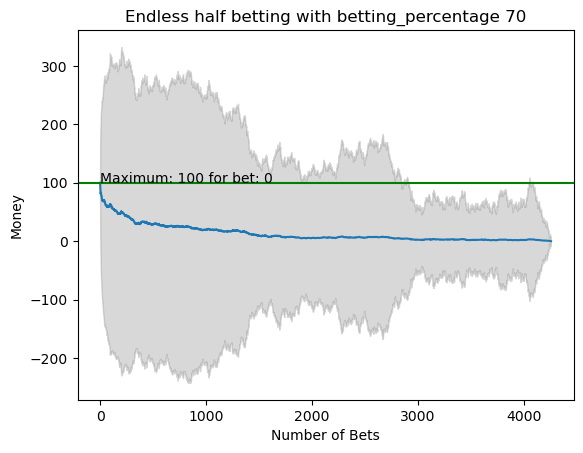
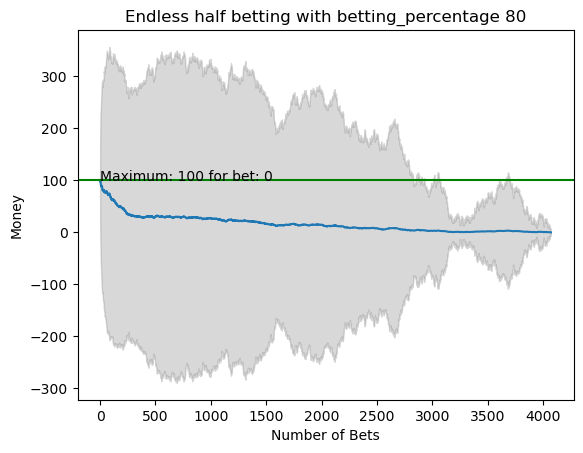
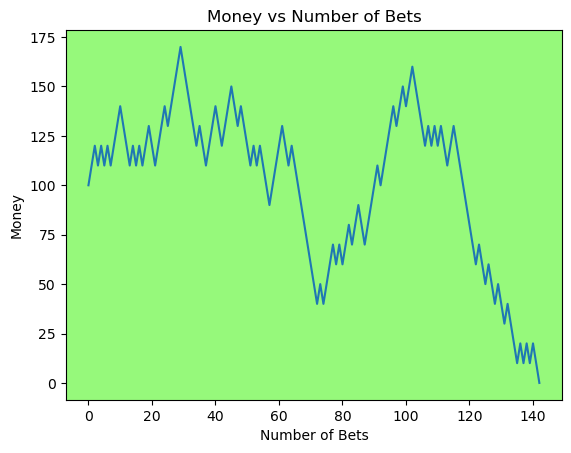
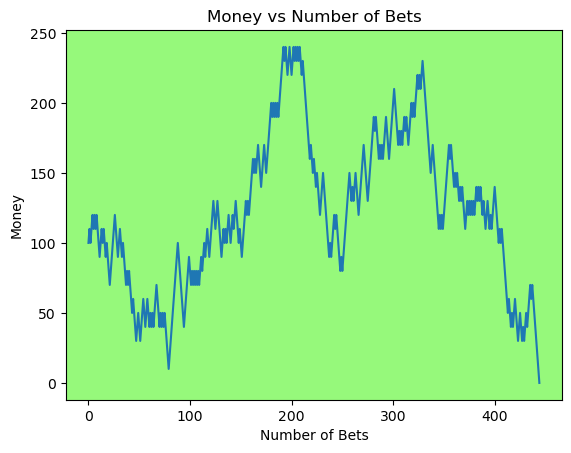
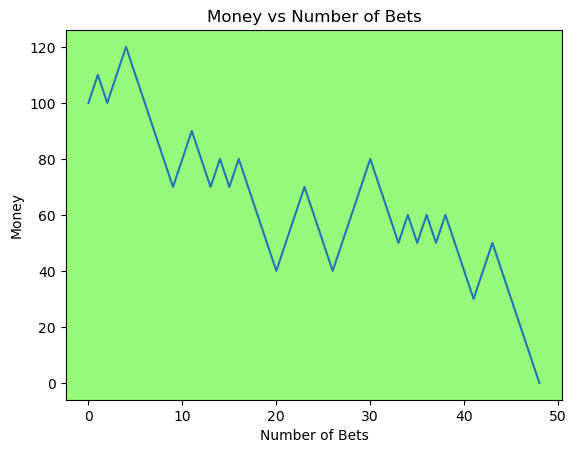
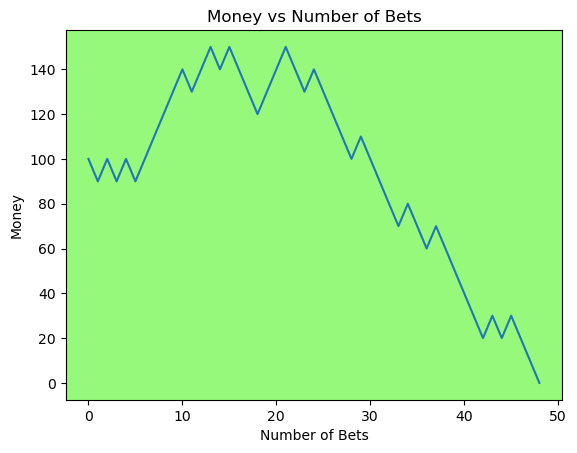
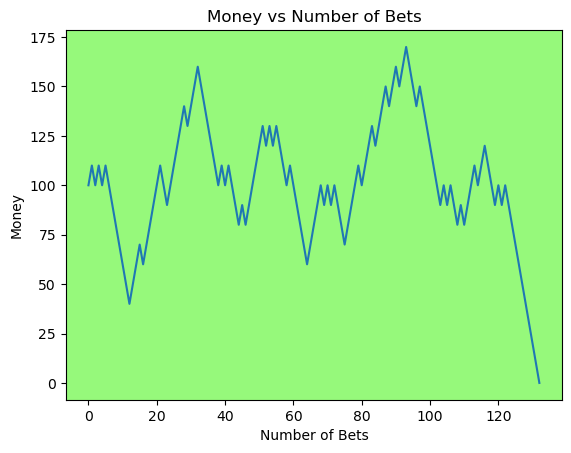
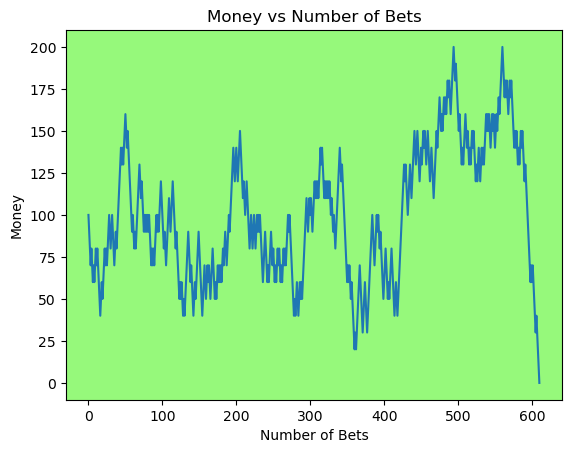
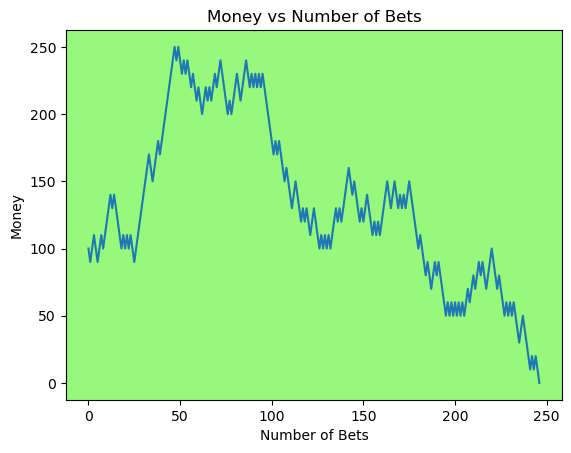
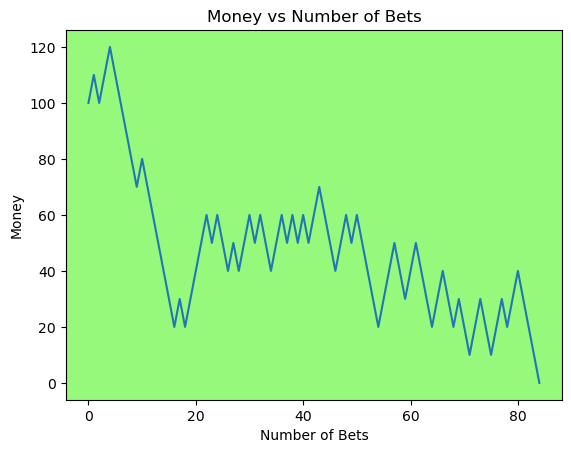
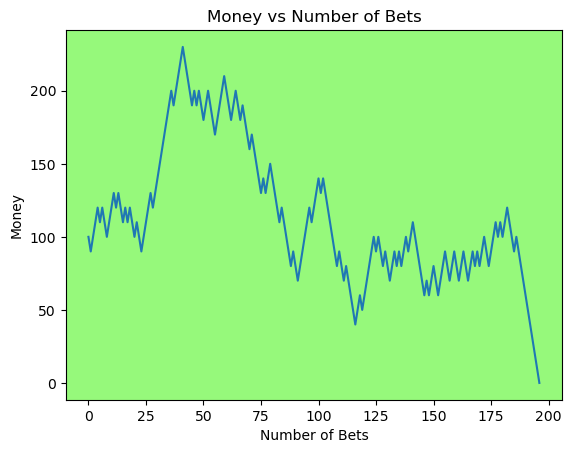
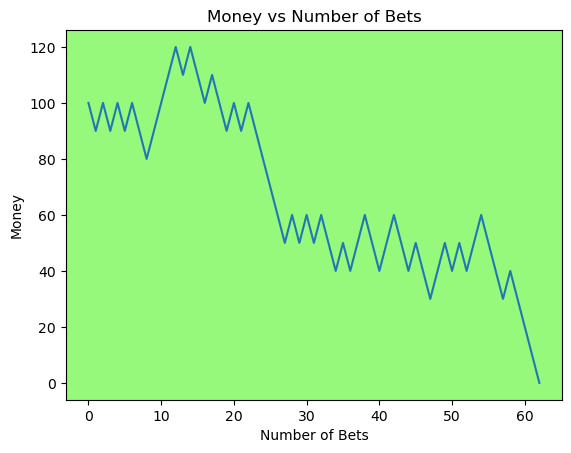
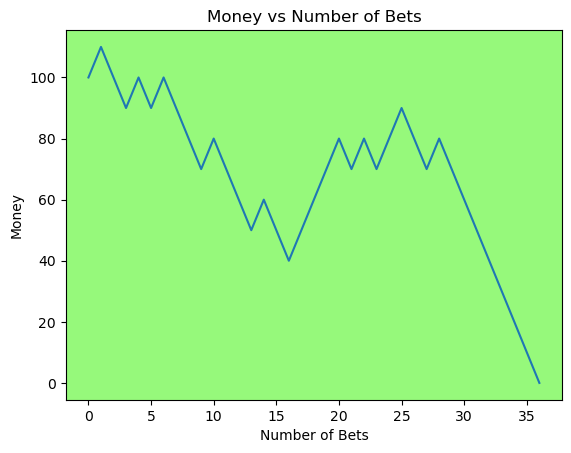
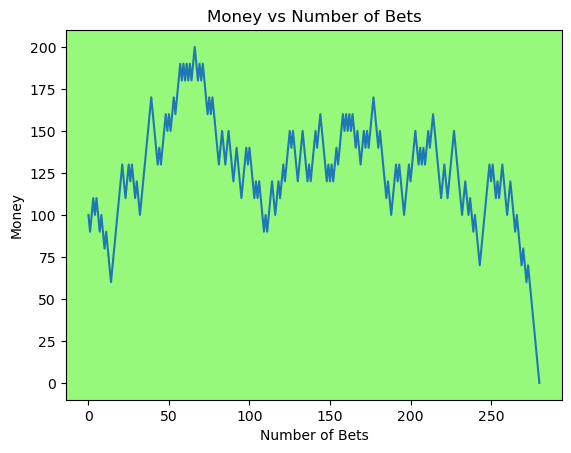
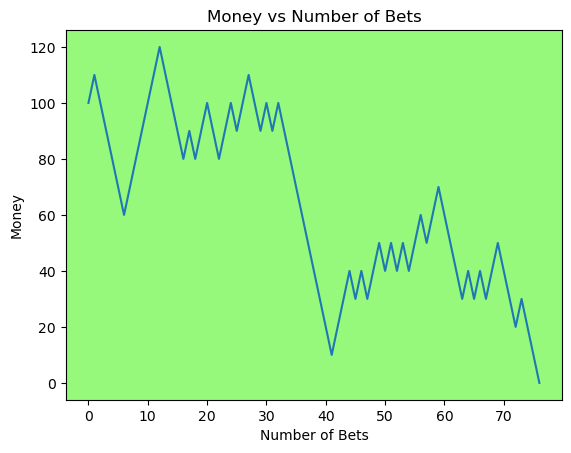
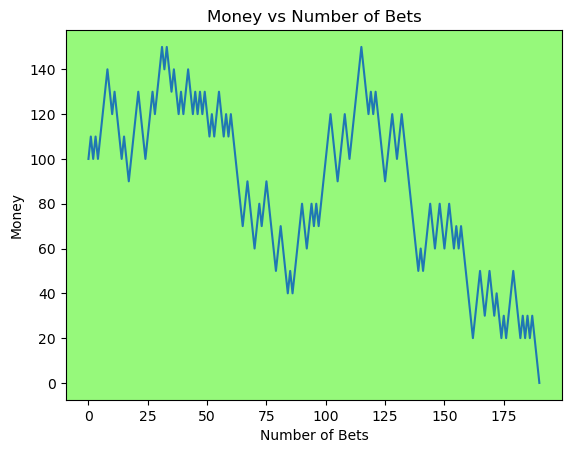
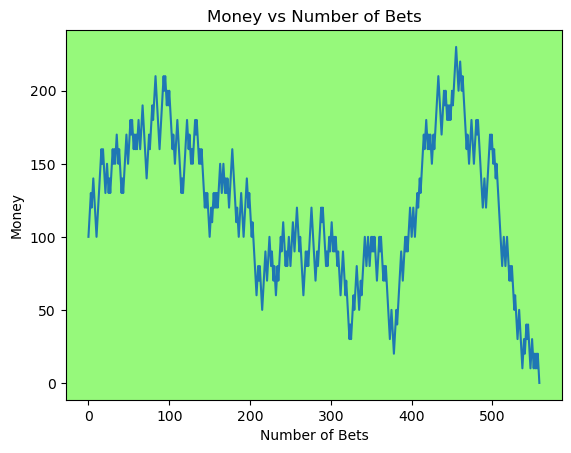
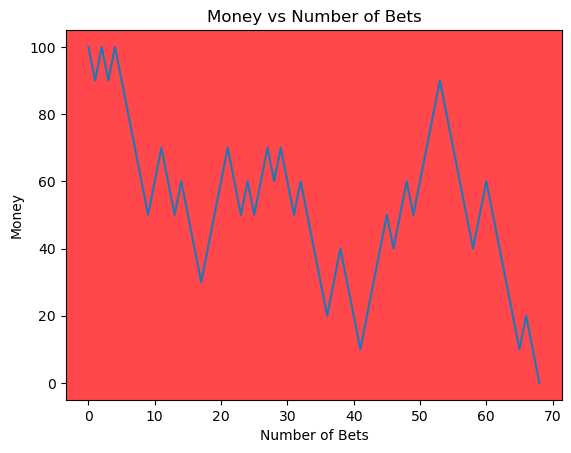
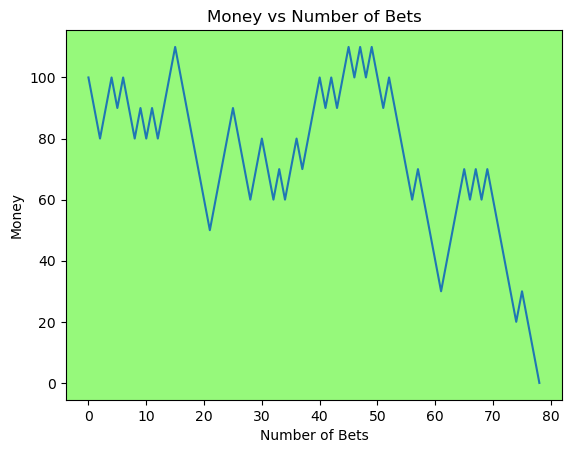
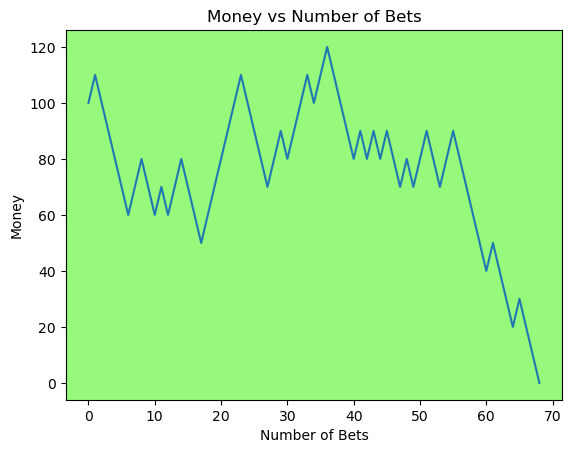
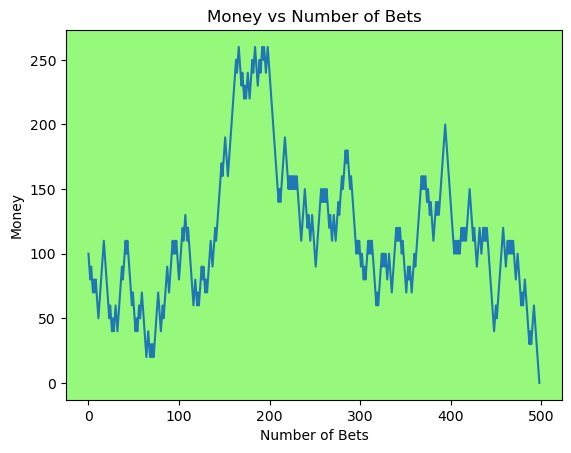
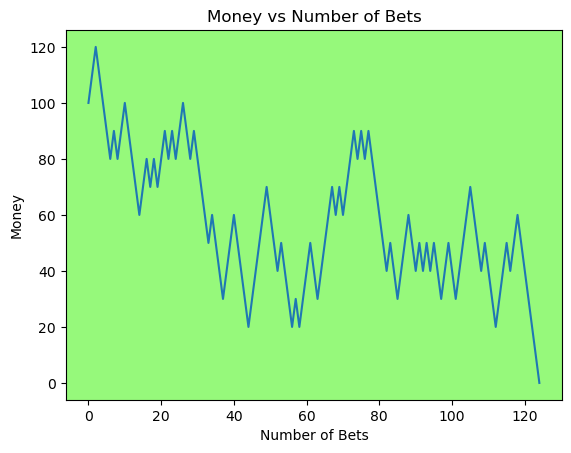
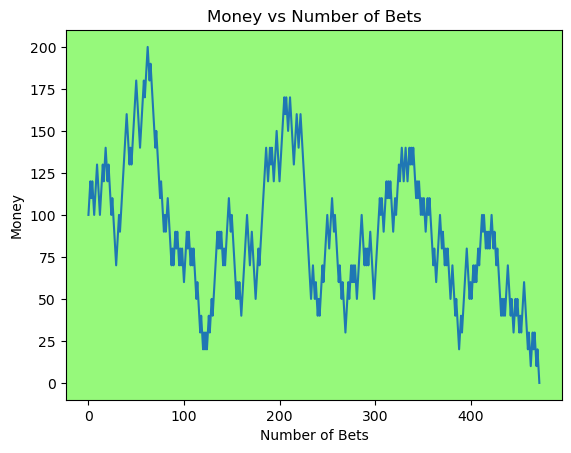
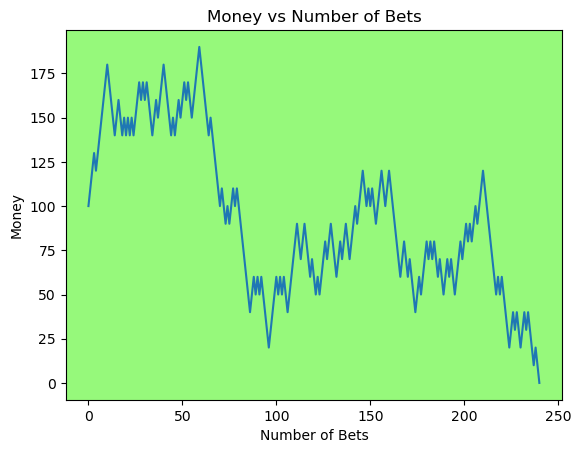
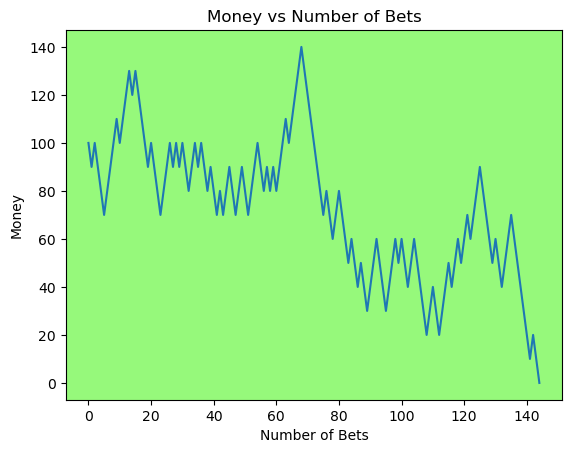
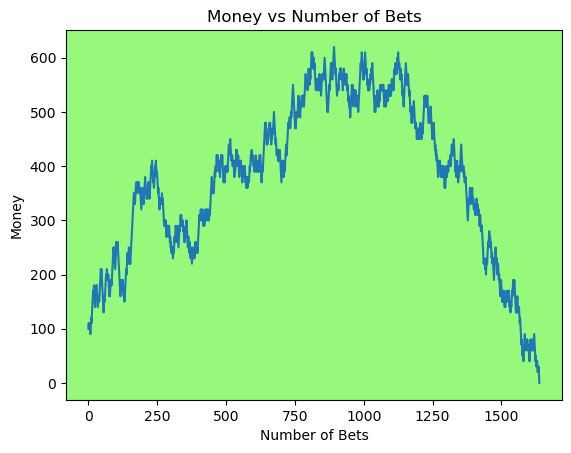
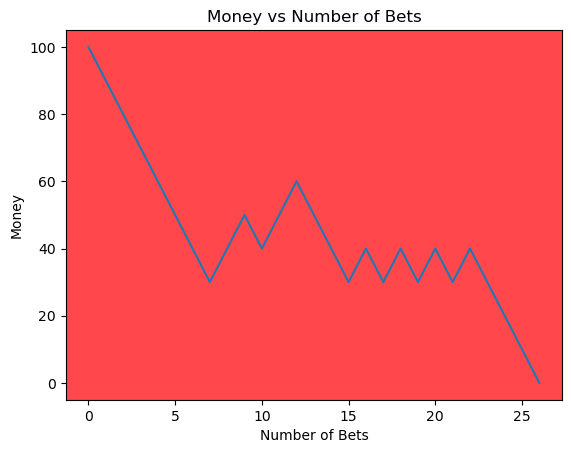
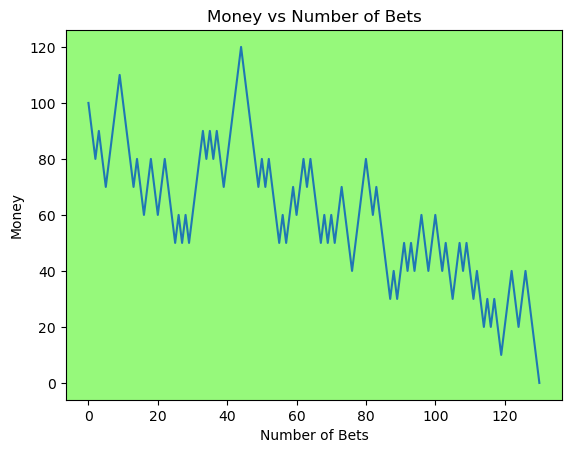
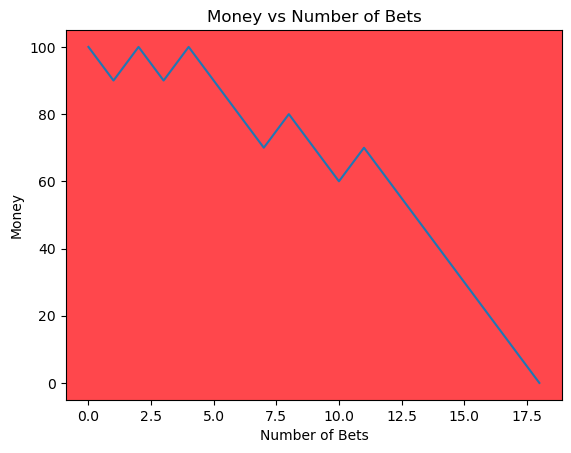
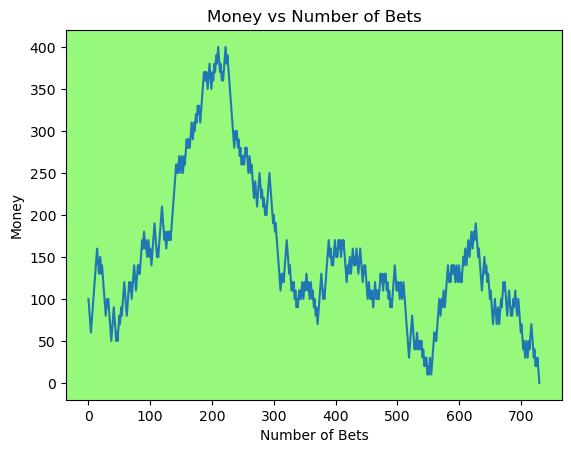
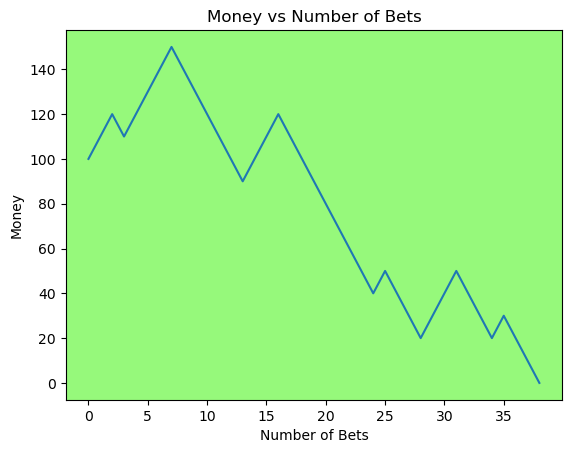
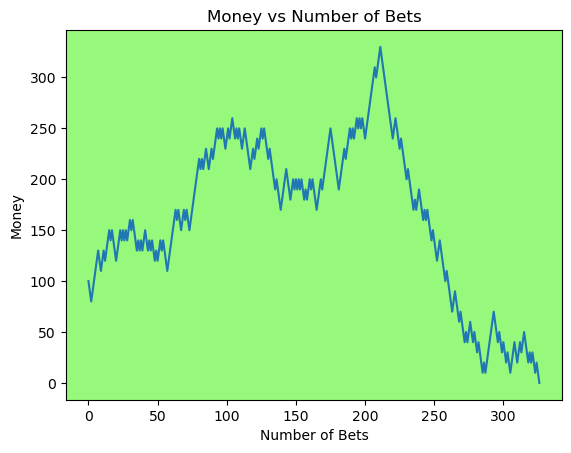
for i in range(50):
money_history = money_histories[10][i]
plot_money_history(money_history, change_colors=True)
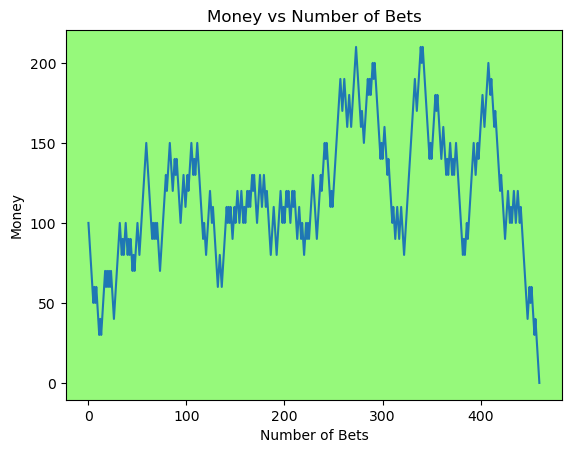
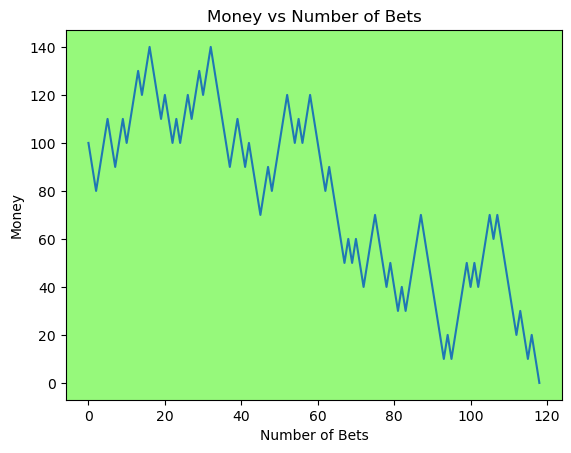
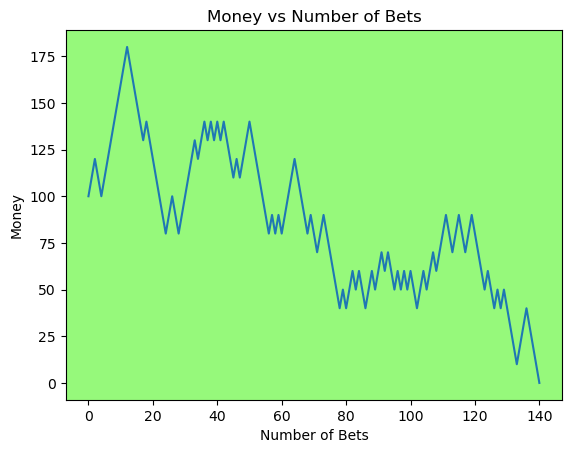
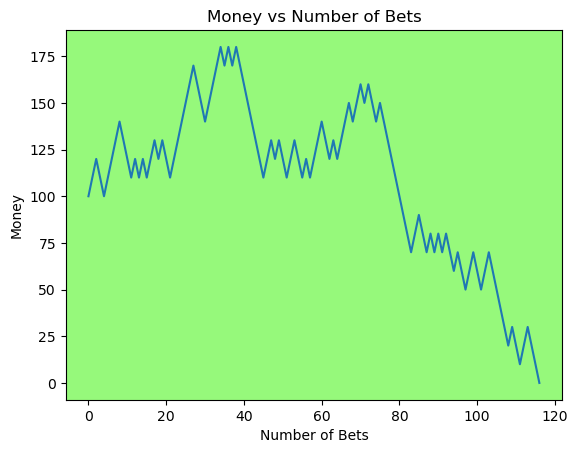
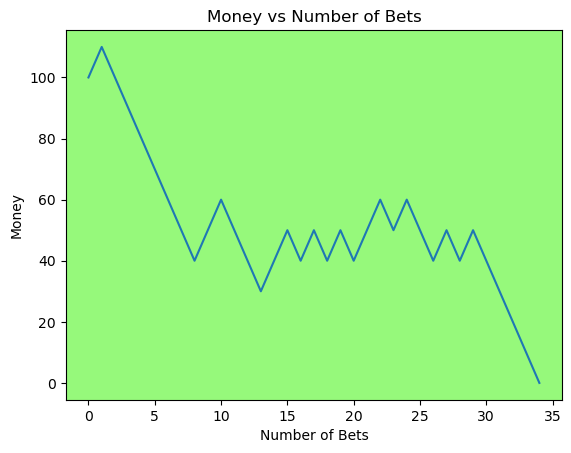
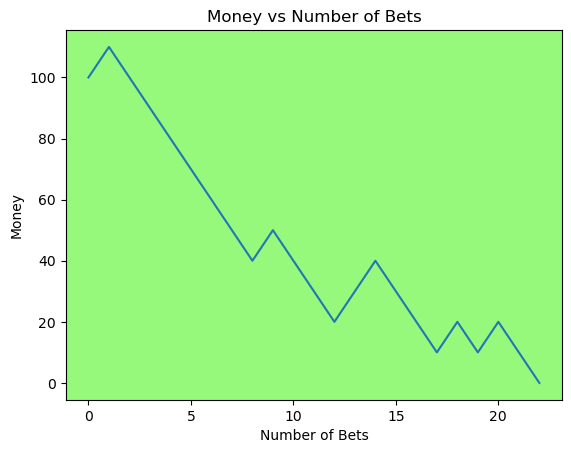
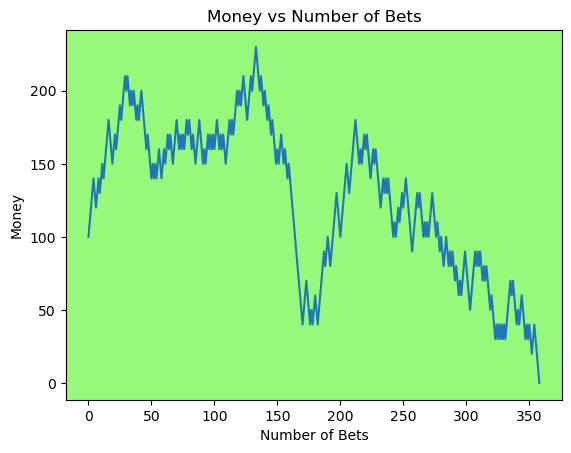
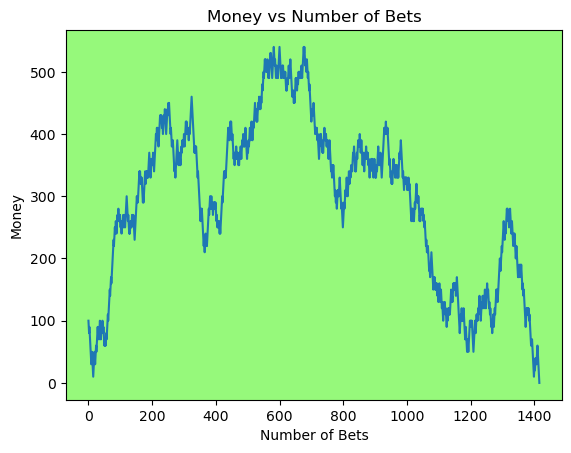
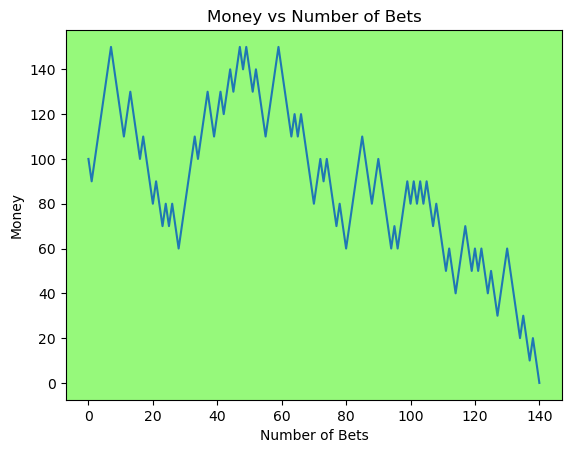
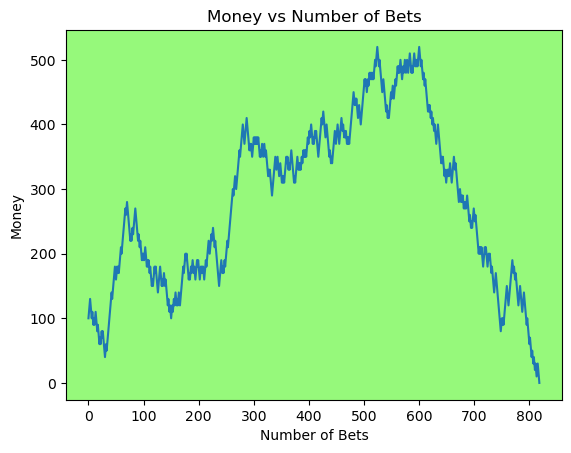
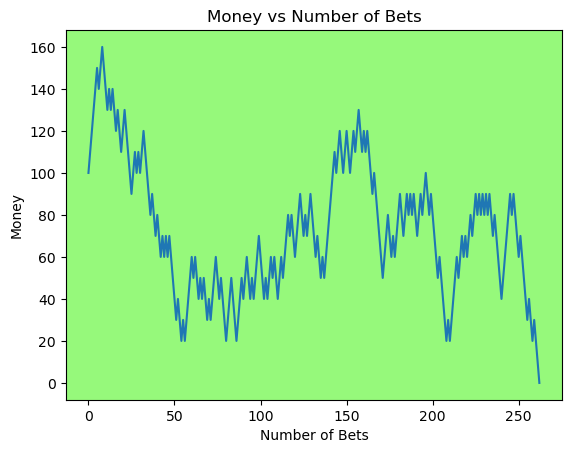
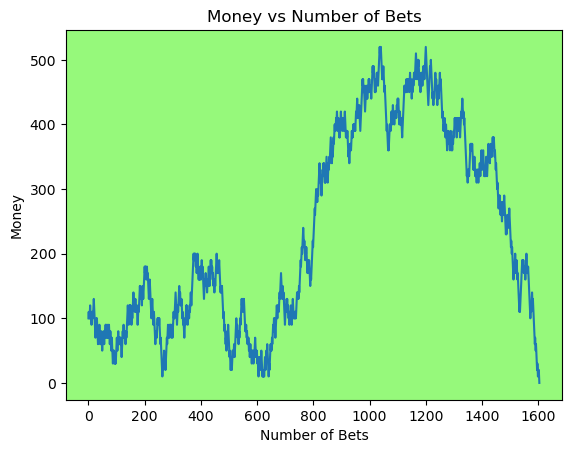
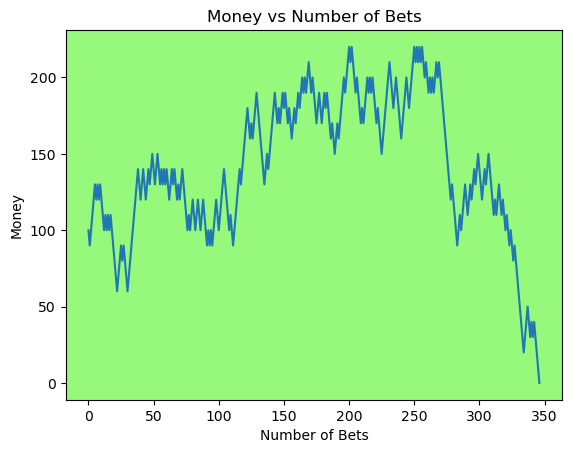
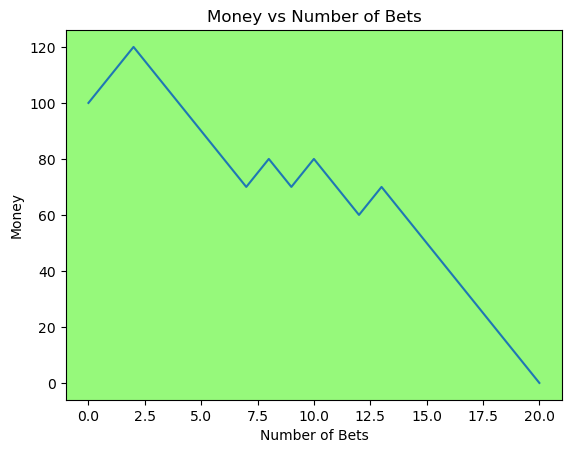
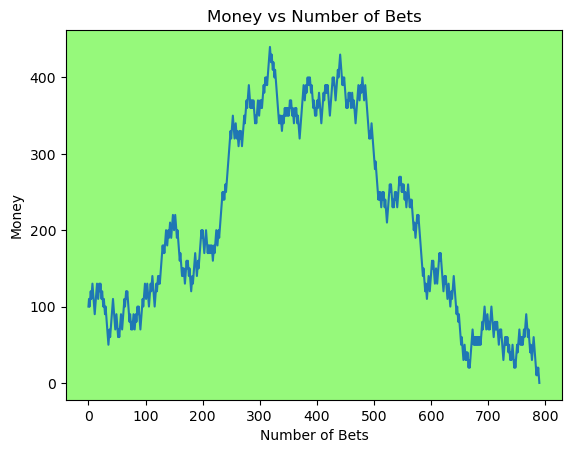
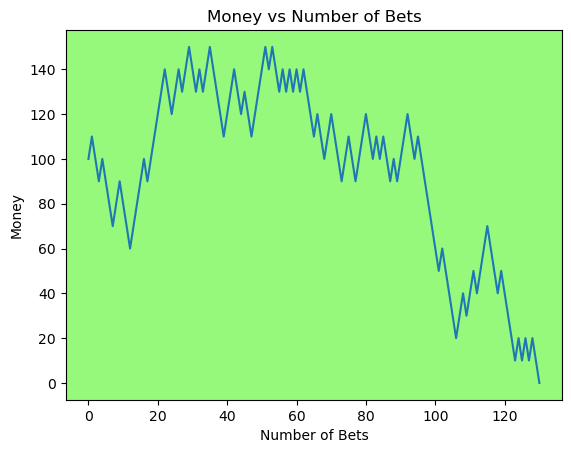
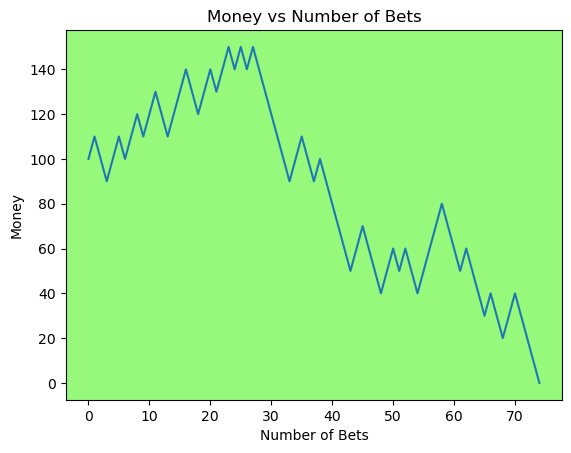
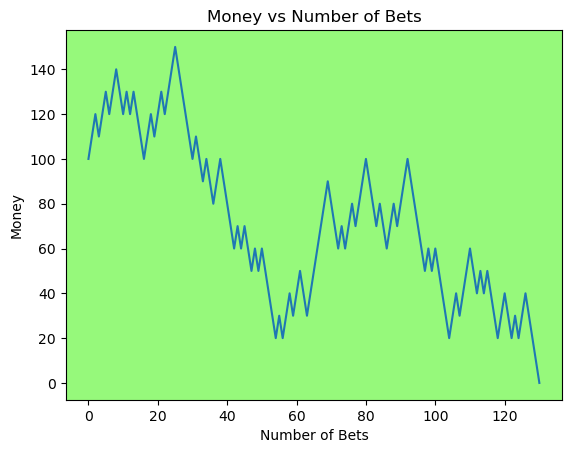
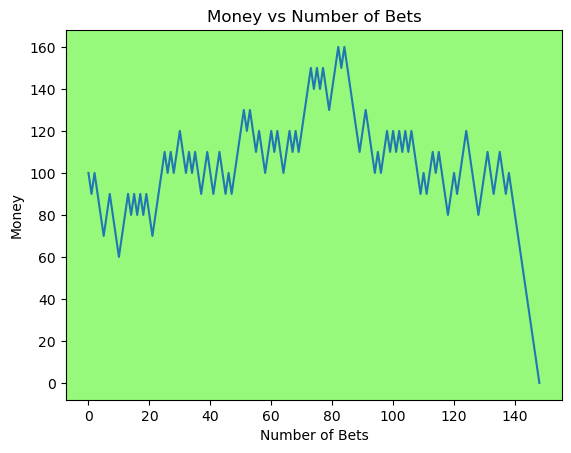
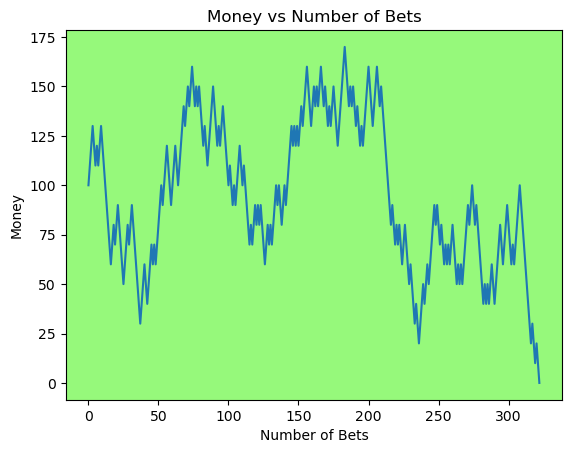
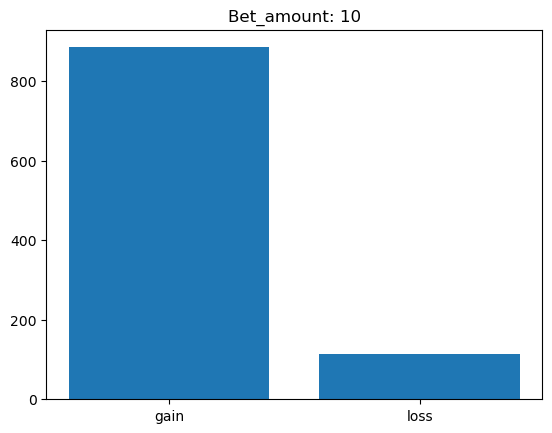
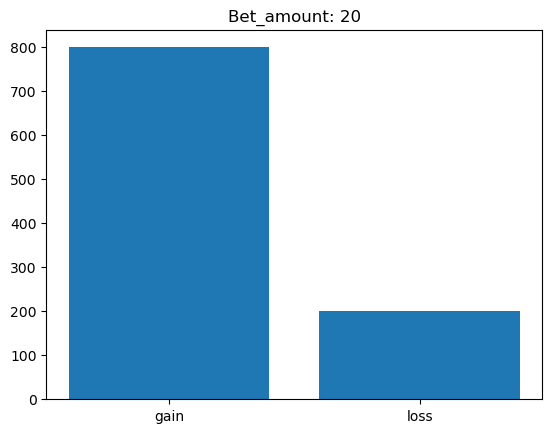
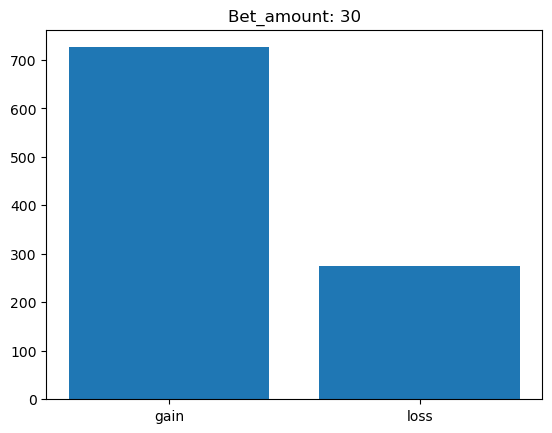
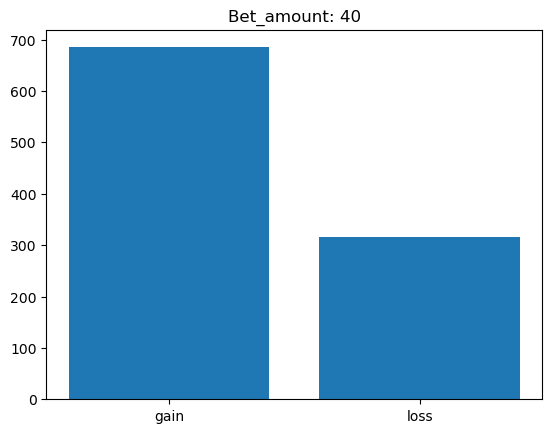
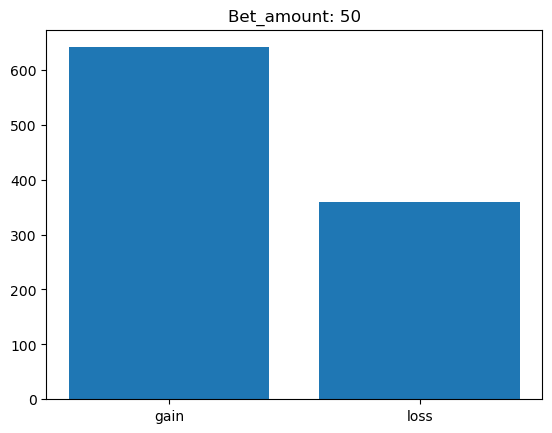
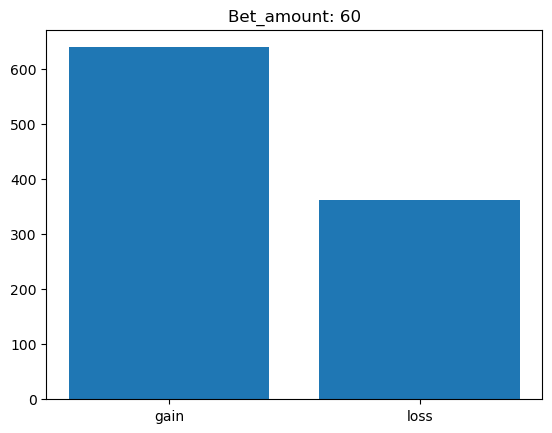
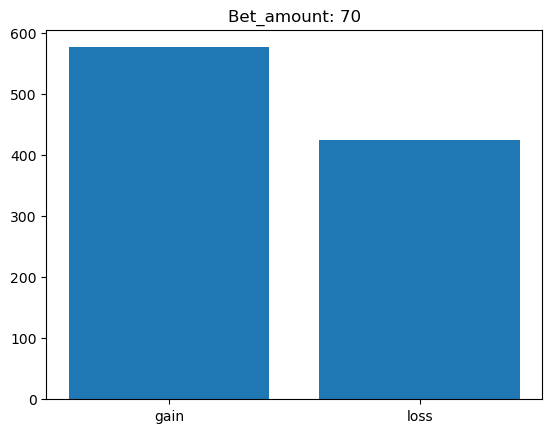
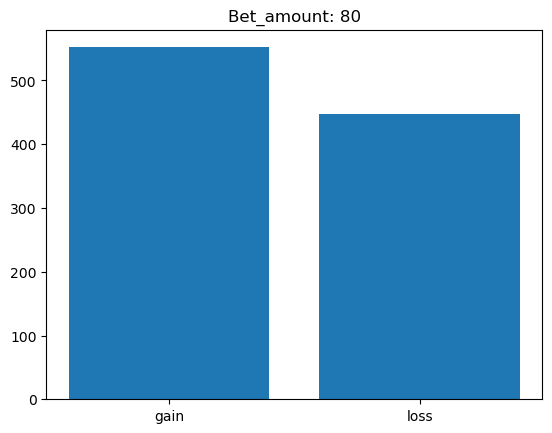
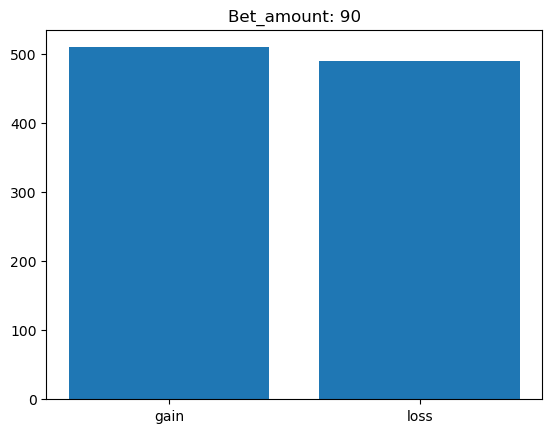
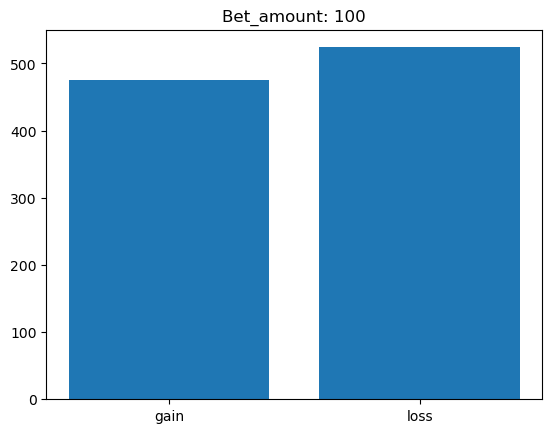
Simulating whether there was a gain at some point#
What is checked is whether there was a point where the balance was greater than the initial balance.
for bet_amount in range(10, 110, 10):
gain, loss = 0, 0
for money_history in money_histories[bet_amount]:
if gain_at_some_point(money_history):
gain += 1
else:
loss += 1
plt.bar(['gain', 'loss'], [gain, loss])
plt.title(f'Bet_amount: {bet_amount}')
plt.show()
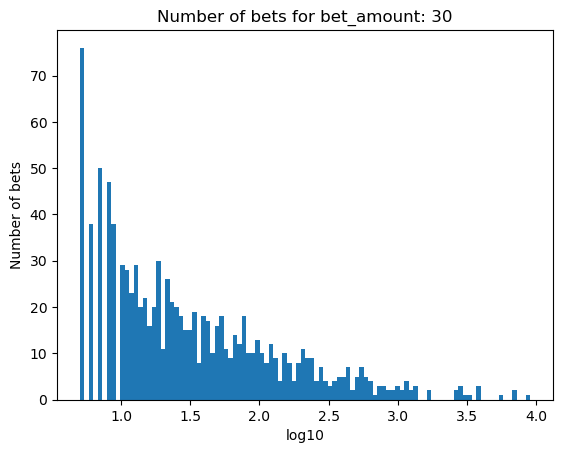
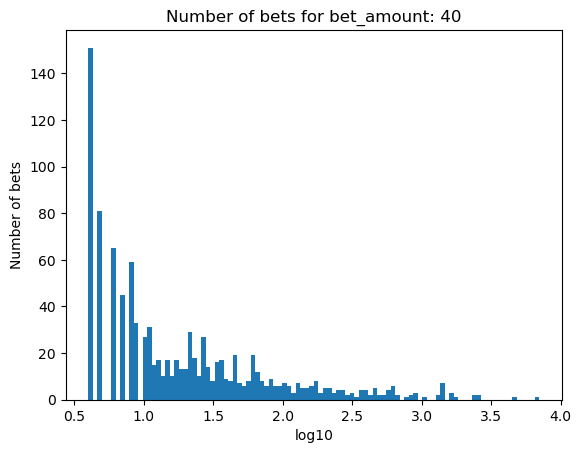
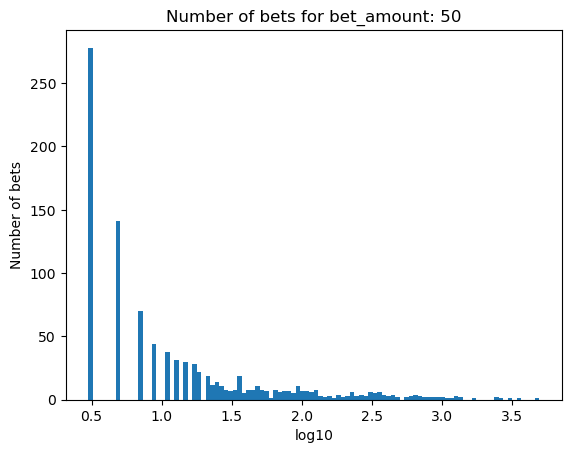
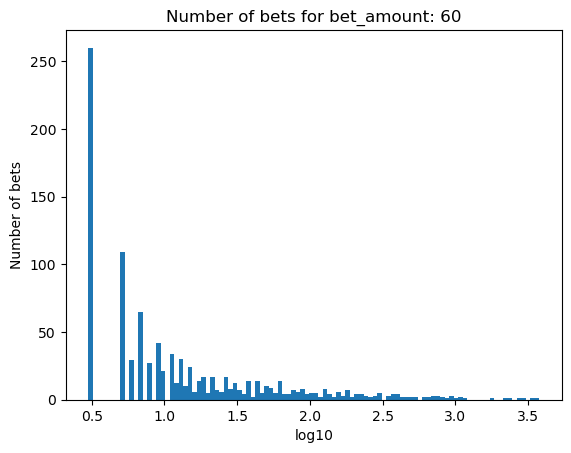
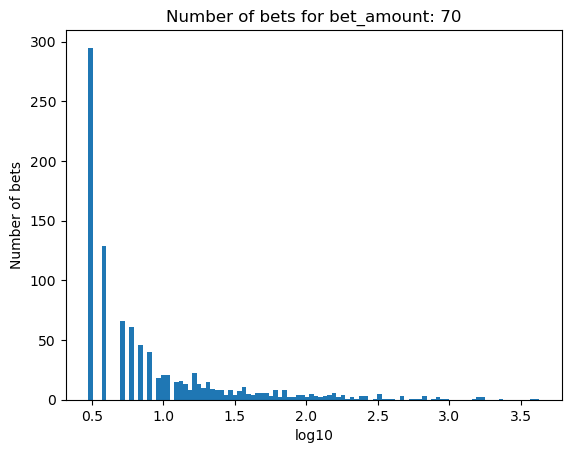
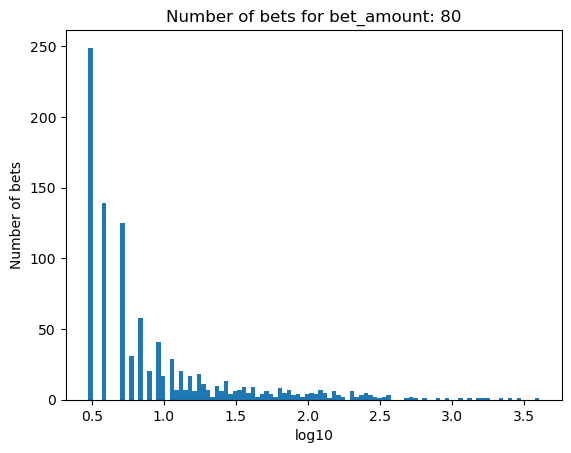
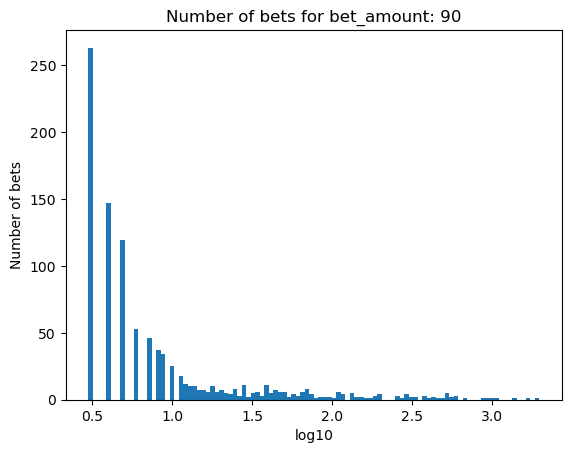
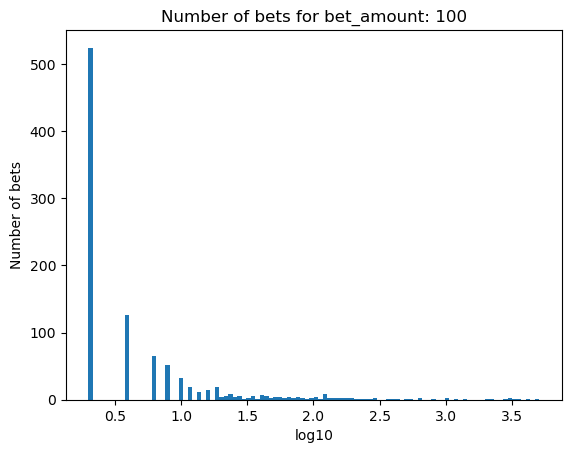
Simulating how many bets are needed for bankruptcy, depending on the percentage of the initial balance that is bet#
for bet_amount in range(30, 110, 10):
plot_number_of_bets(money_histories[bet_amount], f'Number of bets for bet_amount: {bet_amount}')